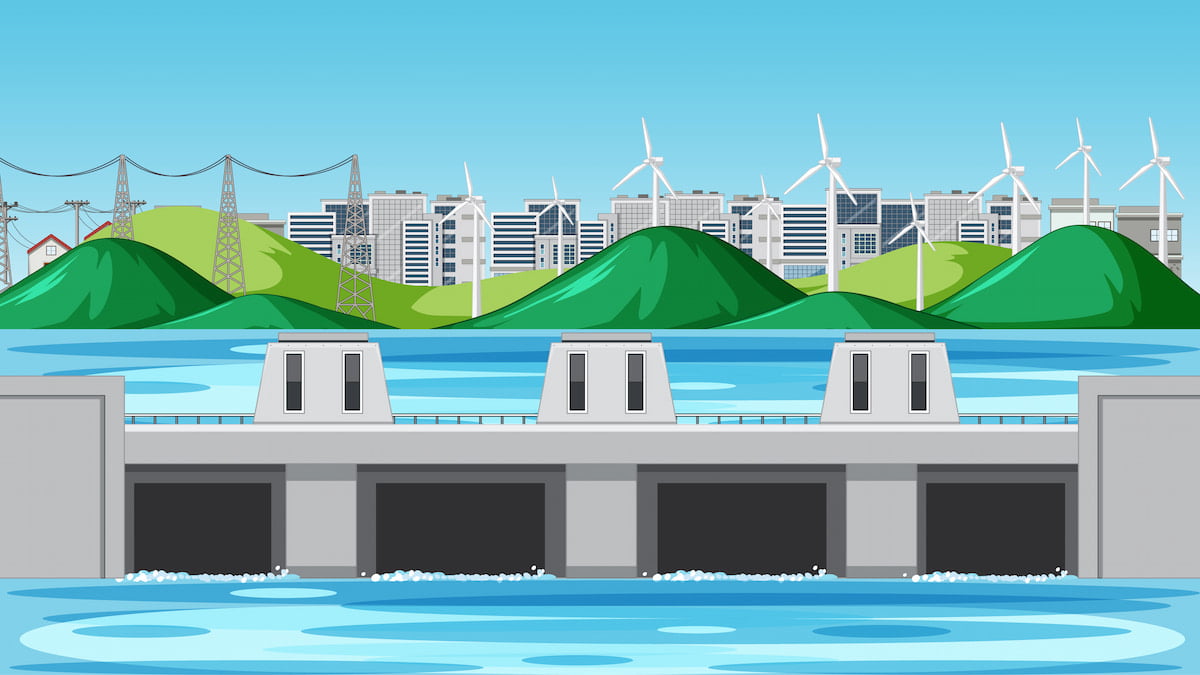
In our quest for clean and sustainable energy solutions, we often look to the natural world for inspiration. Hydropower and ocean energy are two examples of renewable energy sources derived from the power of water. These technologies harness the energy of moving water to generate electricity, offering a promising alternative to fossil fuels.
Table of Contents
Hydropower: A Proven Source of Renewable Energy
Hydropower is the most mature and widely used renewable energy source, generating about 16% of the world’s electricity. It harnesses the energy of moving water, typically through dams built across rivers. As water flows through the dam, it turns turbines, which in turn generate electricity.

There are two main types of hydropower plants:
- Reservoir hydropower plants: These plants use dams to store large amounts of water in reservoirs. The water is then released through turbines to generate electricity.
- Run-of-the-river hydropower plants: These plants use the natural flow of water in rivers to generate electricity. They do not have reservoirs, so they are limited by the amount of water flowing in the river.
Hydropower has several advantages, including:
- It is a mature and well-understood technology.
- It is a reliable source of energy, with predictable output.
- It has a low carbon footprint.
However, hydropower also has some disadvantages, including:
- It can be expensive to build and maintain dams.
- Dams can disrupt ecosystems and displace communities.
- Climate change can affect the amount of water available for hydropower generation.
Ocean Energy: Tapping into the Untapped Potential
Ocean energy is a relatively new and emerging technology with the potential to provide a significant amount of clean energy. There are several different ways to harness the energy of the ocean, including:
- Tidal energy: This technology harnesses the energy of the tides to generate electricity. Tidal barrages are built across estuaries, and the water flowing in and out of the barrage turns turbines.
- Wave energy: This technology harnesses the energy of waves to generate electricity. Wave energy converters are placed in the ocean and convert the motion of the waves into electricity.
- Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC): This technology harnesses the temperature difference between the surface and deep ocean to generate electricity.
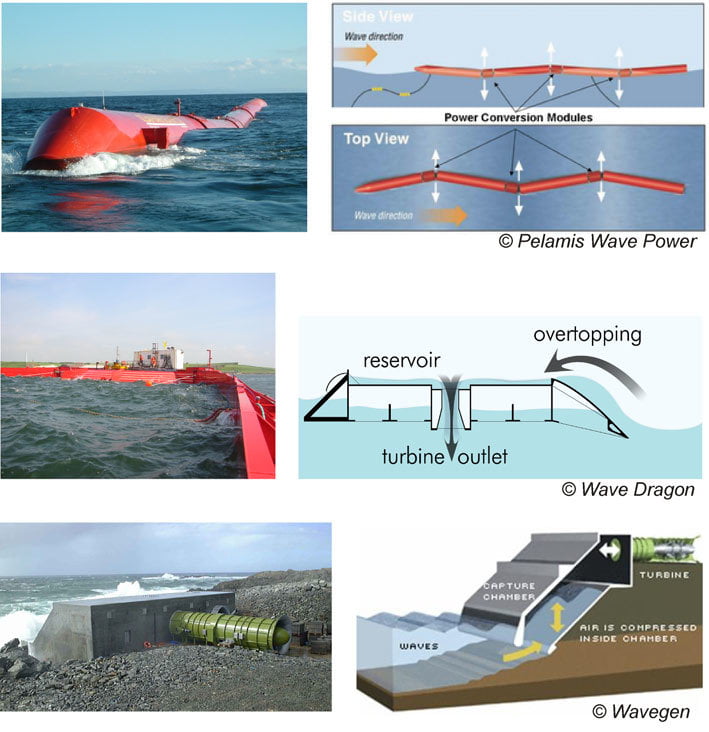
Ocean energy has several advantages, including:
- It is a vast and untapped resource.
- It has a low impact on the environment.
- It is not limited by land availability.
However, ocean energy also has some disadvantages, including:
- It is a relatively new technology and is still under development.
- It can be expensive to build and maintain ocean energy converters.
- The technology is not yet commercially viable in many places.
The Future of Hydropower and Ocean Energy
Hydropower and ocean energy are both promising renewable energy sources with the potential to play a significant role in the future of our energy mix. As technology continues to improve and costs decrease, these technologies are likely to become more widely adopted.
Beyond the Text: Exploring Hydropower and Ocean Energy
To learn more about hydropower and ocean energy, I encourage you to explore the following resources:
- The International Hydropower Association: https://www.hydropower.org/
- The World Ocean Council: https://www.oceancouncil.org/
- The European Ocean Energy Association: https://www.oceanenergy-europe.eu/
I hope this blog post has provided you with a helpful overview of hydropower and ocean energy. As we continue to develop these technologies, they have the potential to make a significant contribution to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Additional Resources
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
- Hydropower and Other Water Energy Technologies: https://www.energy.gov/eere/water/hydropower-program
- Wave power: https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/
- Hydropower and Ocean Energy: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8274374
Thank you for reading!

